-
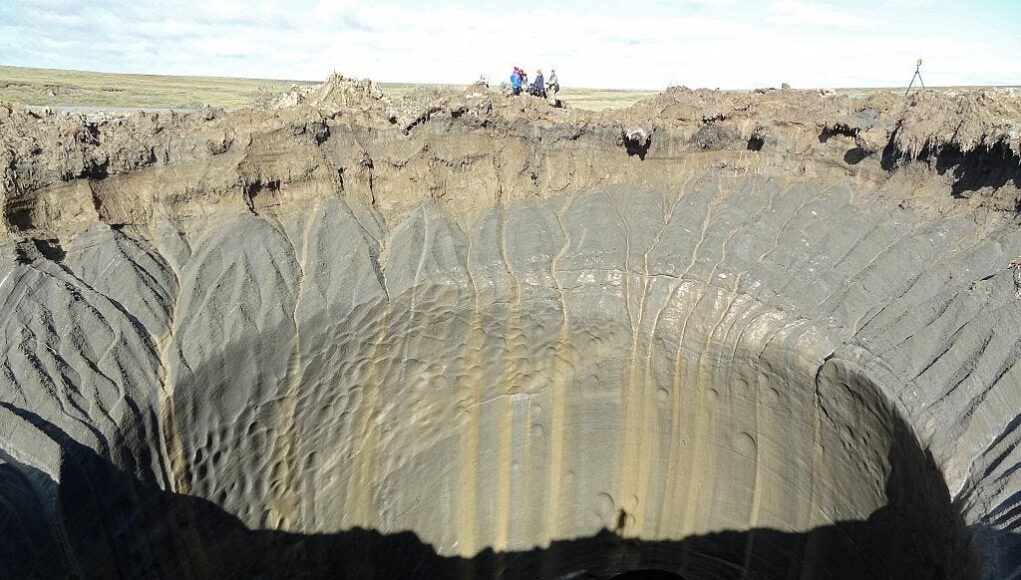
Scientists supplied a brand new clarification for the large craters that maintain showing in Siberia.
-
These craters, first noticed in 2012, could be greater than 160 toes deep and over 65 toes vast.
-
They could be as a result of sizzling time bombs product of pure gasoline increase beneath the frozen floor.
Scientists are placing ahead a brand new clarification for the giant exploding craters that appear to be randomly showing within the Siberian permafrost.
These craters, first noticed in 2012, have been popping up within the abandoned Siberian permafrost, puzzling scientists.
They are often substantial, reaching greater than 160 toes in depth and 65 toes in width, and blasting chunks of particles lots of of toes away.
Some stories have recommended the blasts can be heard 60 miles away.
Now scientists are proposing that sizzling natural gas seeping from underground reserves is likely to be behind the explosive burst.
The findings may clarify why the craters are solely showing in particular areas in Siberia.
The realm is thought for its huge underground reserves of pure gasoline, the examine’s lead creator Helge Hellevang, who’s a professor of environmental geosciences on the College of Oslo in Norway, advised Enterprise Insider.
“When local weather change or ambiance warming is weakening the opposite a part of the permafrost, then you definately get these outbursts — solely in Siberia,” he mentioned.
Gasoline makes the outlet, but it surely comes from deep reserves
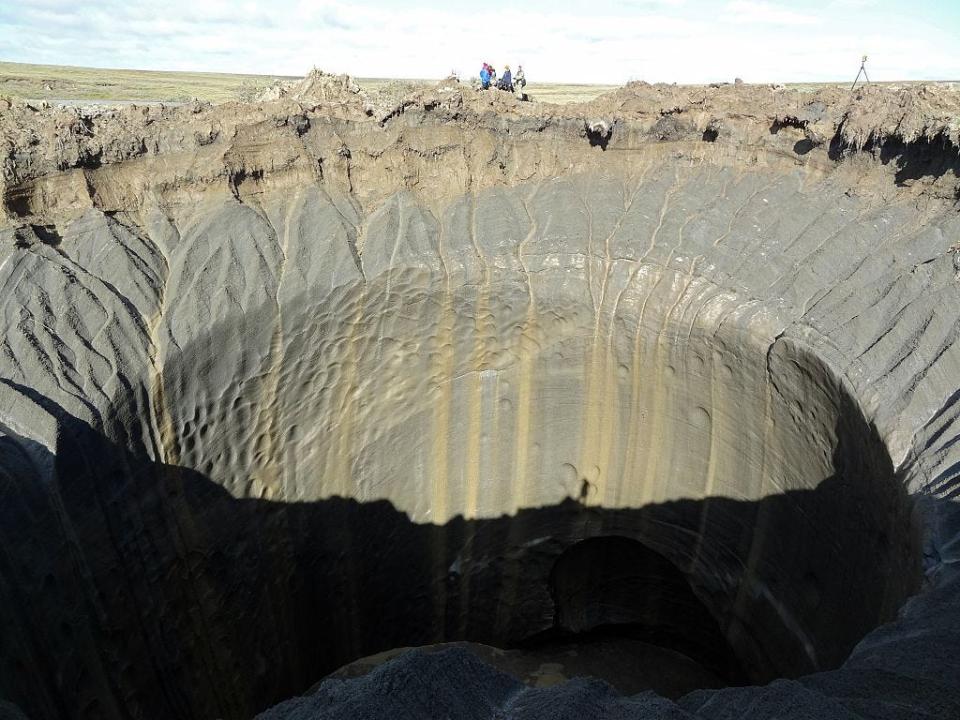

Permafrost traps a variety of natural materials. As temperatures rise, it thaws, permitting that mulch to decompose. That course of releases methane.
So scientists had naturally proposed the methane seeping from the permafrost itself was behind the craters.
This is not a loopy thought. It is notably the method that is thought to result in thermokarsts, lakes that seem in areas the place permafrost is melting, which bubble with methane and could be lit on fireplace.

However that does not clarify why the so-called exploding craters are so localized.
Solely eight of those craters have been recognized up to now, all inside a really particular space: the Western Siberian Yamal and Gydan peninsulas in Northern Russia.
Exploding lakes, in contrast, are seen in all kinds of areas the place permafrost is discovered, together with Canada.
Hellevang and his colleagues counsel there’s one other mechanism at play: sizzling pure gasoline, seeping up via some form of geological fault, is increase beneath the frozen layer of soil and heating the permafrost from beneath.
These sizzling gasoline plumes would assist thaw the permafrost from the underside, making it weaker and extra prone to collapse.
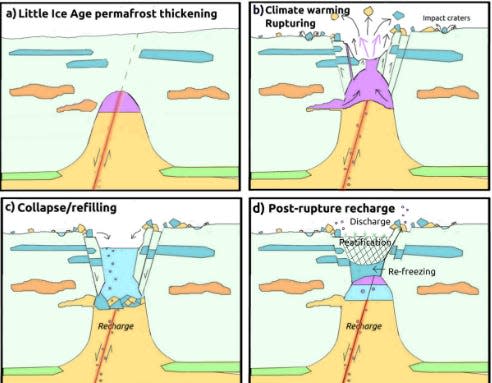
“This explosion can solely occur if the permafrost is skinny and weak sufficient to interrupt,” mentioned Hellenvang.
Rising temperatures soften the higher layer of the permafrost on the identical time. This creates the right circumstances for the gasoline to be freed abruptly, triggering both an explosion or a “mechanical collapse” brought on by the gasoline, which is beneath strain.
That creates the crater, Hellevang and colleagues are suggesting.
The realm is rife with pure gasoline reserves, which traces up with Hellevang and colleagues’ concept, per the examine.
“This space is among the largest petroleum provinces on the earth,” he mentioned.
In keeping with the scientist’s mannequin, extra of those craters may have been created and have since disappeared as close by water and soil fell in to fill the hole.
“It is a very distant space, so we do not actually know the true quantity,” he mentioned.
“If you happen to have a look at the satellite tv for pc picture of the Yamal Peninsula, there are millions of these spherical plate-like depressions. Most or all of them may have been thermokarsts, however probably they is also earlier craters which have shaped,” he mentioned.
The speculation was printed on the net server EarthArXiv last month. The article has not but been validated by a evaluation from scientific friends.
A harmful speculation for the local weather disaster
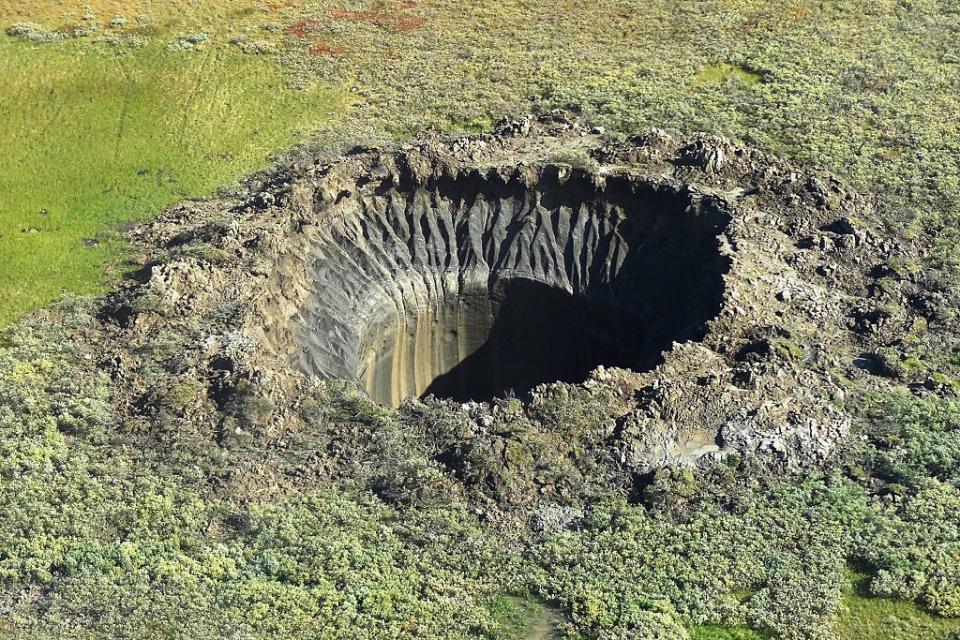

Whereas the thought has advantage, extra proof will likely be wanted to point out these reserves of gasoline are constructing beneath the permafrost, Lauren Schurmeier, an Earth scientist on the College of Hawai’i who researches the subject, advised New Scientist.
Nonetheless, if the speculation is discovered to be appropriate, this might spell bother for local weather fashions.
Pure gasoline is stuffed with methane, a potent greenhouse gas. This might imply the craters are performing like big chimneys via which the damaging chemical might be freed abruptly into the ambiance, Thomas Birchall on the College Centre in Svalbard, Norway, advised New Scientist.
“If that is the usual manner that giant accumulations fail then you definately’re dumping a variety of methane in a really brief time,” he advised New Scientist.
Hellenvang, nevertheless, exercised warning. If this phenomenon solely exists on this very restricted space, it could be that the affect is minute on a world scale. Whereas there may be possible a considerable amount of methane saved in underground reserves, it is not clear how a lot of that might get out.
“I believe what we have to do is perceive at the beginning how a lot methane is of course leaking from these form of methods, after which evaluate that to how a lot methane that’s truly inside the permafrost for natural matter,” Hellenvang mentioned.
“Then we are able to have a extra practical finances on how a lot could be launched due to atmospheric heating or local weather change,” he mentioned.
Learn the unique article on Business Insider
At present Information High Newsmaac










